LLMs - 101
- Gabriel Pinto
- Llm
- May 21, 2024
- 8 min
- Medium Link
Table of Contents
In this post we are going to discuss the multitude of LLMs with brief explanations on how they work and how you can find one that fits your main needs.
AI or LLM? Understanding the difference
In simple terms:
- AI = broader concept. Exists for decades and it’s in our lives for a while, like: Alexa / Siri, Instagram recommending stuff you said 5 minutes ago, Google Translator, Boston Dynamics building robots since the 90’s and to end this endless list predicting cancer in 2015 - yes, 9 years ago, maybe I’m bald now - by using machine learning to analyze photos
- LLM = a reaaaally small portion of AI. It’s using one method of AI to complete one single task: predicting words based on a provided context 😄.
Text-to-speech and image generation are other AI methods but not LLMs.
If you’re interested in how these other AI methods work, let us know!
How LLMs Work?
Before diving into the details, here’s a cool fact:
What if I told you that the mathematical and statistical foundations of LLMs exist for decades?
They do. LLMs rely on Markov chains, Bayesian inference and neural networks. All of them are there for years. What really made a difference those past few years was having GPUs and TPUs (Graphics Processing Units and Tensor Processing Units). Those enabled the ability to train a LLM with massive datasets and, equally important, computing your response in near real-time!
Also, this enabled more complex math and statistical operations and developments too!
But now, LLM 101:
- MASSIVE datasets (I see you Reddit selling data for everyone);
- Calculations. How a computer will breakdown the texts of the dataset - tokens, how tokens will be transformed into vectors and matrices full of numbers and how the probabibility of token x given context y will be calculated;
- Training the model. Now you know the probability of each token x given context y;
Now you participate!
- User input: You will open chatGPT and input a question;
- Tokenization: All the calculations will take place. First of all, Open(not so open)AI will break your question into tokens;
- Embedding: Transforming those tokens into the vectors and matrices. Your question will start to looking like this:
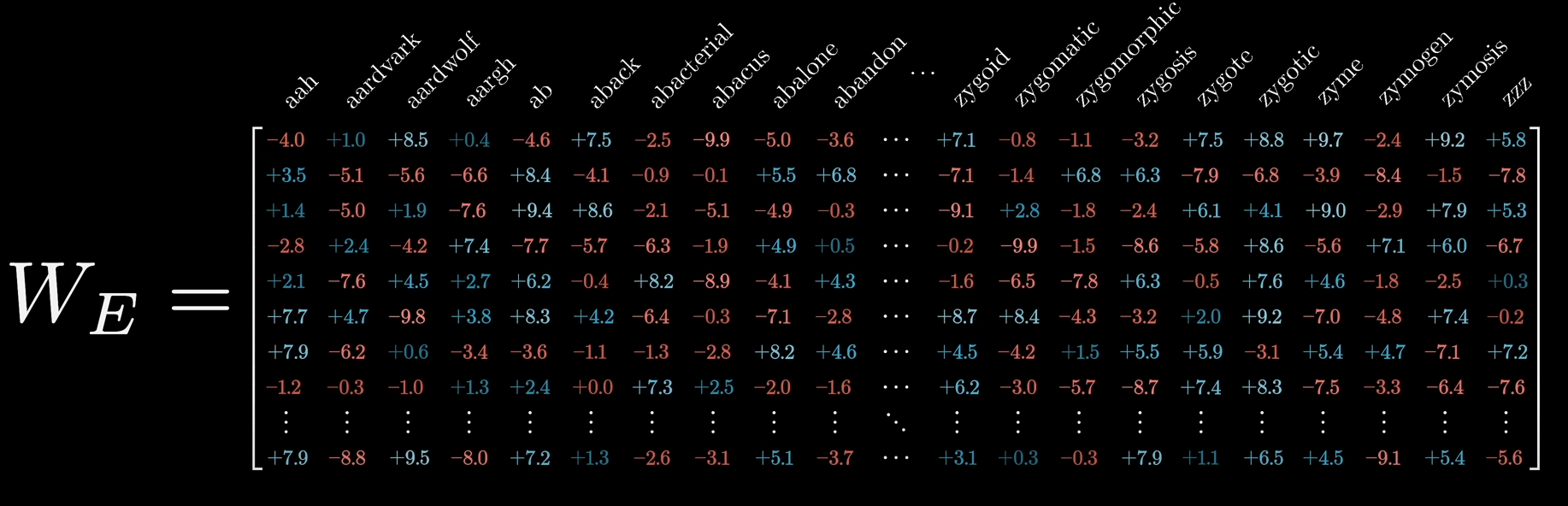 from really cool video to explain how LLM works
from really cool video to explain how LLM works - Inference: Calculating “probability of token x given your question y”. Basically your embedded matrix will be multiplied by a terribly large matrix that represents the trained model and will have the n closest tokens to your question;
- Do it over and over: Redo it until you have an answer;
- Unembedding: Unembed the response, tokens stiil need to be transformed into works, cause I hope no one here has already become an AI and now is reading vectors on the street.
What I should look for a LLM?
Well done, now you know how LLMs work!
However, you couldn’t give a smaller crap for it. You just wanna use and it’s totally fair.
Everything from now on is focused on maximizing which LLMs you use in your day-to-day activities at work or at home.
I really do believe there are a large amount of people that:
- Are having difficulties with LLM costs;
or
- Could actually use better suited LLMs for their uses.
LLM Features
Let’s start by the main features different LLMs might have.
A great tip to compare different LLMs is artificialanalysis.ai . Most of the LLM and LLM providers features that I will explain in this article are represented and compared in this AMAZING website.
Quality
It means how well the LLM answers you. Currently there are several different methods to measure the LLM quality and each of them optimize by a certain area.
For example:
- MMLU -> evaluate the performance of multilingual models. That means: how it can answer several questions about several areas of knowledge. P.S.: it’s measure only question-answer bases; and it’s the one that tbey leave the LLM to solve SAT and see how well it goes.
- MT-Bench -> it evaluates on a multi-turn question based. Close to MMLU, but how it’s multi-turn, it measures best if the LLM can follow instructions
- HumanEval -> this one is much more focused on generating code!
.. and a lot more methods.
From artificialanalysis.ai we can see that Claude 3 Opus, Gemini 1.5 Pro and LLama 3 (70B) can provide a comparable quality to GPT-4 Turbo.
I’ll probably have to create an article only for GPT-4o haha!
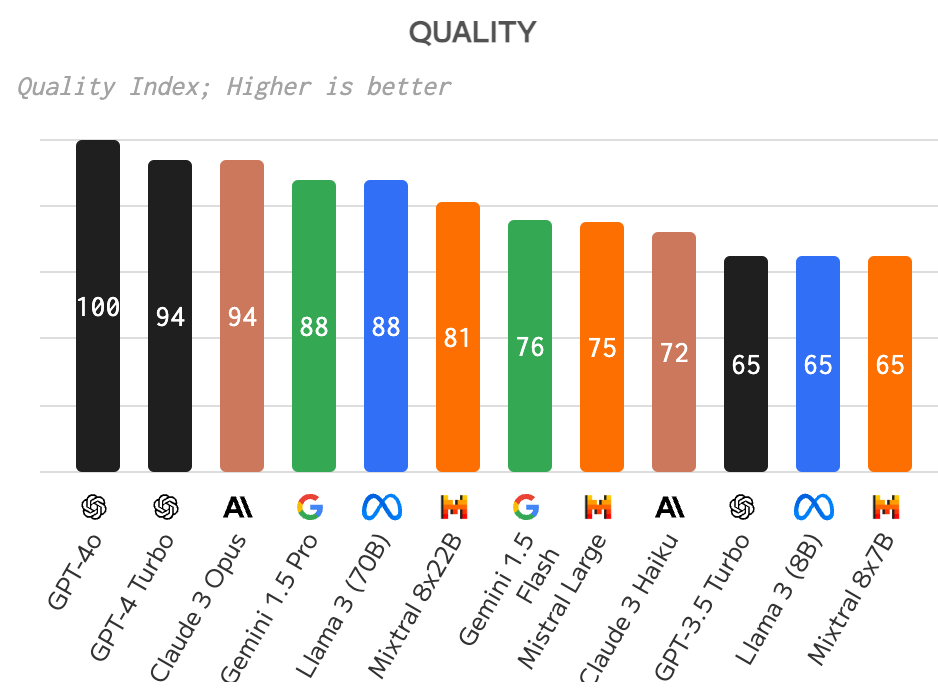 main LLMs quality comparison
main LLMs quality comparison
But you can also check that the MMLU score is much much tied between the best LLM.
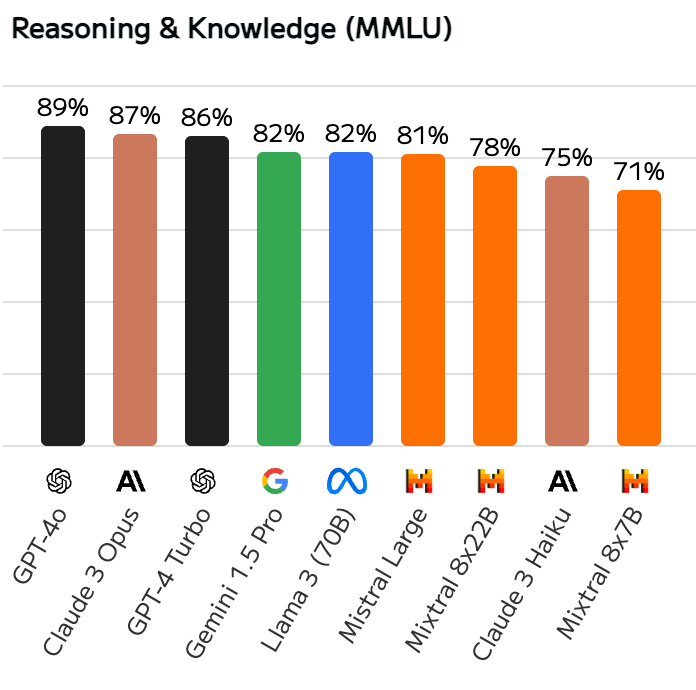 main LLMs MMLU score comparison
main LLMs MMLU score comparison
That means: if you are only using for generic tasks (no code generation), you would probably be good with ANY of them.
Speed
Understand LLM speed as: how much tokens/words the LLM can output per second.
It was cooler to debate 2 weeks ago when GPT-4o didn’t exist. But speed is a big component when you are choosing a LLM to use.
How many times you were like: “bro, GPT just answer me, pls!” And then refreshing tabs and then seeing that you’ll have to redo the prompt.
Also, for a large infrastructure and assistants towards clients, you’ll always prefer something with the capability of answering faster.
A cool exercise is looking at this comparison and seeing:
- HOW FLIPPING FAST IS GPT-4o compared to all models with high quality scores;
- HOW EVEN MORE FLIPPING FAST are smaller models like Gemini 1.5 Flash and Llama 3 (8B).
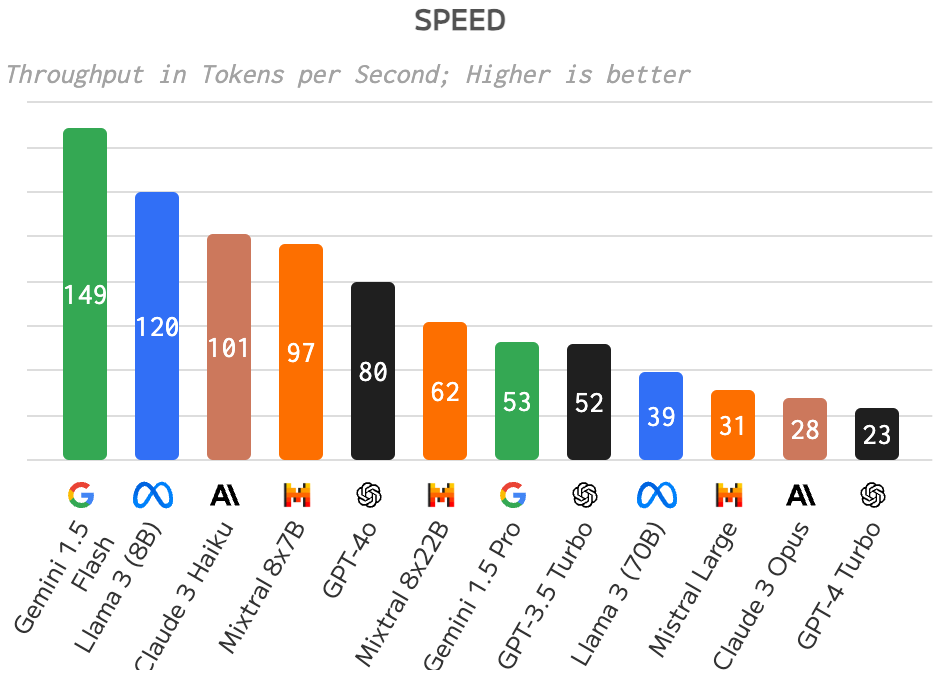 main LLMs MMLU score comparison
main LLMs MMLU score comparison
So once again, there’s a huge opportunity if your tasks are fairly simple. You could use one of those smaller models that will answer much faster and you will be just fine.
Source (open or closed)
Before a table of pros and cons. Just a context on open and closed models.
Closed models -> one created a LLM and is hiding what’s the training data and how the model works for themselves. Examples: ClosedAI GPT4 or Anthropic models Open models -> one created and shared with the community. Example: Meta LLama models (Zuck ❤️) and some Mistral models (🇫🇷 ❤️ - chatGPT of Mistral is literally LeChat).
For this one, a simple table should do the trick.
| Areas | Pros and Cons |
|---|---|
| Cost | You can deploy open models in your own infrastructure. It is only cheaper if you can setup and maintain it well. But at the same time there are a lot of API providers for open models. |
| Speed | This one is trickier and I think will be clear when I talk about API providers in the following section. But I will say open models have a small lead here. |
| Innovation | There’s an entire community (search for hugging face) doing lots of stuff. Here there’s an opportunity of being able to find models re-trained by someone in the world that will perform perfectly for your use-case. Also: uncensored models 😆 use it in your own discretion. |
| Support | Here it is good to rely in the good old capitalism. You pay, you get nice support! |
| Customization | In open models you can re-train the entire model as you wish! In closed ones you are limited to RAGs and fine-tunings. |
| Security | Here we have two sides: one is having the confidence that the LLM will not respond with things it shouldn’t – closed models excel here; the other is ensuring that what your users input is securely stored – this is similar to costs, if you have excellent data security, open models will work better, as you will have control over everything. |
| Social Wellfare | We need open LLMs! |
Yes, I’m probably biased.
LLM Providers Features
In my opinion this section is the most important one in the entire post. By far.
Most of us, me of a few months ago included, don’t realise that OpenAI, Meta, Mistral, Anthropic, Google and others are mostly LLM developers. Only a part of their responsibility is to create a proper UI and API for you to use it.
With open models, there is the possibility of several companies to work on how they can deploy LLMs in the most efficient manner so you can have the lowest price and fastest speed possible.
The nicest example is groq. They are a hardware startup that are developing a specific design for computing called LPU (Language Processing Unit™) to run LMMs. With that, they can outspeed all competitors by 2x minimum and have in theory more affordable prices per token.
Tip: Open groq and test them. You can run a chatGPT-esque conversation with the top open models for free because besides being the faster, they’re are probably burning cash to win the competition.
UI Features
If you are not a developer and only uses LLM for your personal use, I’d just stick for this section and maybe the Price/Speed ones.
I personally think that OpenAI has no competition in this section. Especially with all the buzz of GPT-4o and there’s no provider that could match the OpenAI chat / playground.
There is the chat itself, you can generate images in the same chat, download documents for it to search, it can search the internet, run code, GPT store and now all the 4o things. It’s simply unfair.
Meta has no playground for Llama, Gemini is well Gemini.. and all the other providers of open models don’t reach OpenAI levels.
What I’ll say though is that if you only use chatGPT for text gen, give a try on groq. At least, you’ll be shocked with the speed.
I’m personally only using chatGPT when things get really hard and basically I want to cut corners on giving him some context with documents (but there’ll an article soon about how I’m fixing this to be 100% independent from GPT).
API Features
Now it’s dev stuff ot at least if you work or rely on devs.
And in here, I do think OpenAI doesn’t have the edge anymore. For developers, using API x or y is simplying a lot, just some lines and an API key.
The only point of attention would be if you need to do a RAG (retrieval augmented generation - when chatGPT searches a document) or a fine-tuning - I won’t even get to re-training a model, that’s another level.
Some providers make RAG and fine-tuning simple. Some others will make it a little complex. Especially RAG once it is required much more frequently than a fine-tuning.
But even with the RAG problem, there already companies like ragapi.com or libraries such as langchain or llama index that make RAG simpler. That’s also a whole entire post on how to build a RAG from scratch.
I mean, once again, some more lines of code.
Price
Aggravating even more the OpenAI case on not having the edge for API services there’s one point I haven’t discussed here: PRICE.
I only wanted to discuss this section because you’ll only pay close attention to this if you’re selling something that uses LLM. If you just use ChatGPT, you don’t need to worry as much.
With the quality and speed comparisons we did earlier + competition on who is the best API LLM provider, prices for open models are CHEAP. The disadvantage for closed models lies in the lack of competition once only them can provide their own models.
Once again, using artificialanalysis.ai I’ll show an example in the price gap between models with similar quality being provided by different companies.
Example: Llama 3 (70B) and it’ll be clear it’s importance for the LLM market.
Remember that the Llama model was scored at 88, GPT4 at 94, Claude 3 Opus at 74 too and Gemini, 88.
Price-wise, Llama is 33x times cheaper than Claude and 16x than GPT-4. Just for perpective, the price to only review this article that I’ve written would be:
Claude: USD 0,12
GPT-4: USD 0,06
Llama-3: USD 0,004
And this is the average price. If you use groq or deepinfra with Llama 3, the cost drops from USD 0.9 per 1M tokens to USD 0.6 (50 times cheaper than Claude).
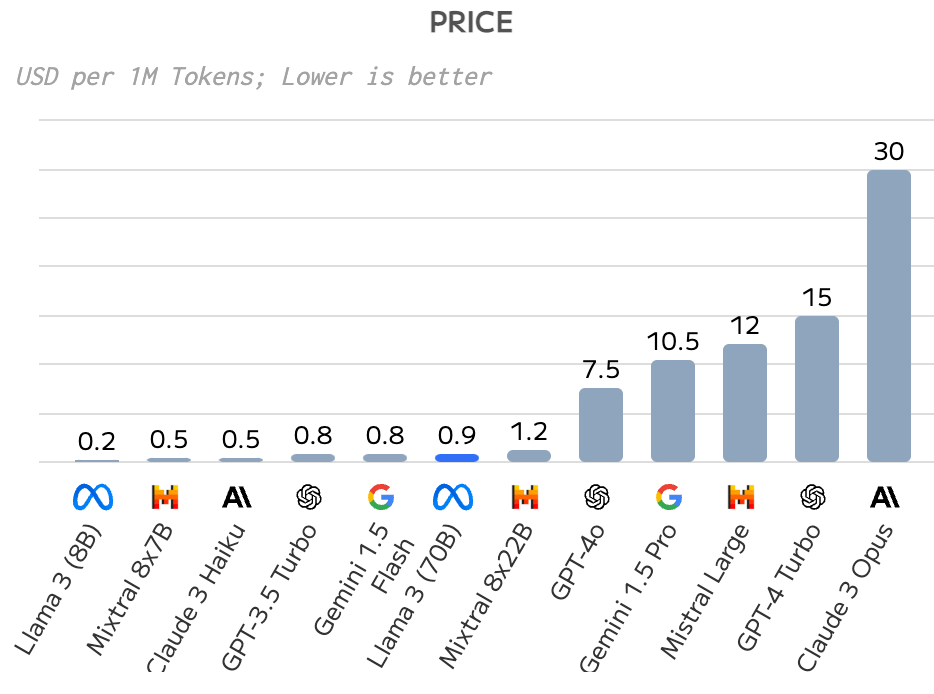 price comparison of LLM models
price comparison of LLM models
Speed
It doesn’t stop there. I’ll mention groq again.
Comparing all LLama 3 (70B) providers, it’s 2x faster than the second one and 15x than the last one (but obviously Microsoft doesn’t want to run Meta’s model fast)
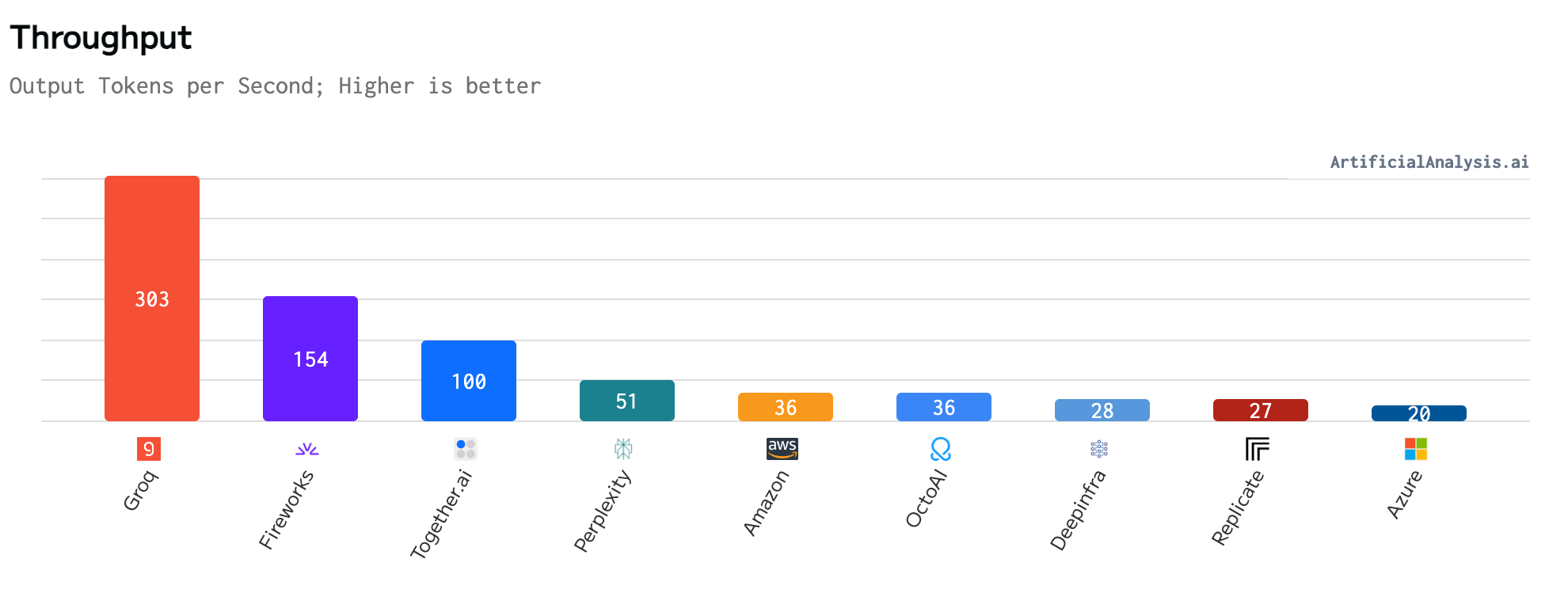 token throughput comparison of LLM models
token throughput comparison of LLM models
Even comparing with GPT4o that is only provided by OpenAI. 3x faster!
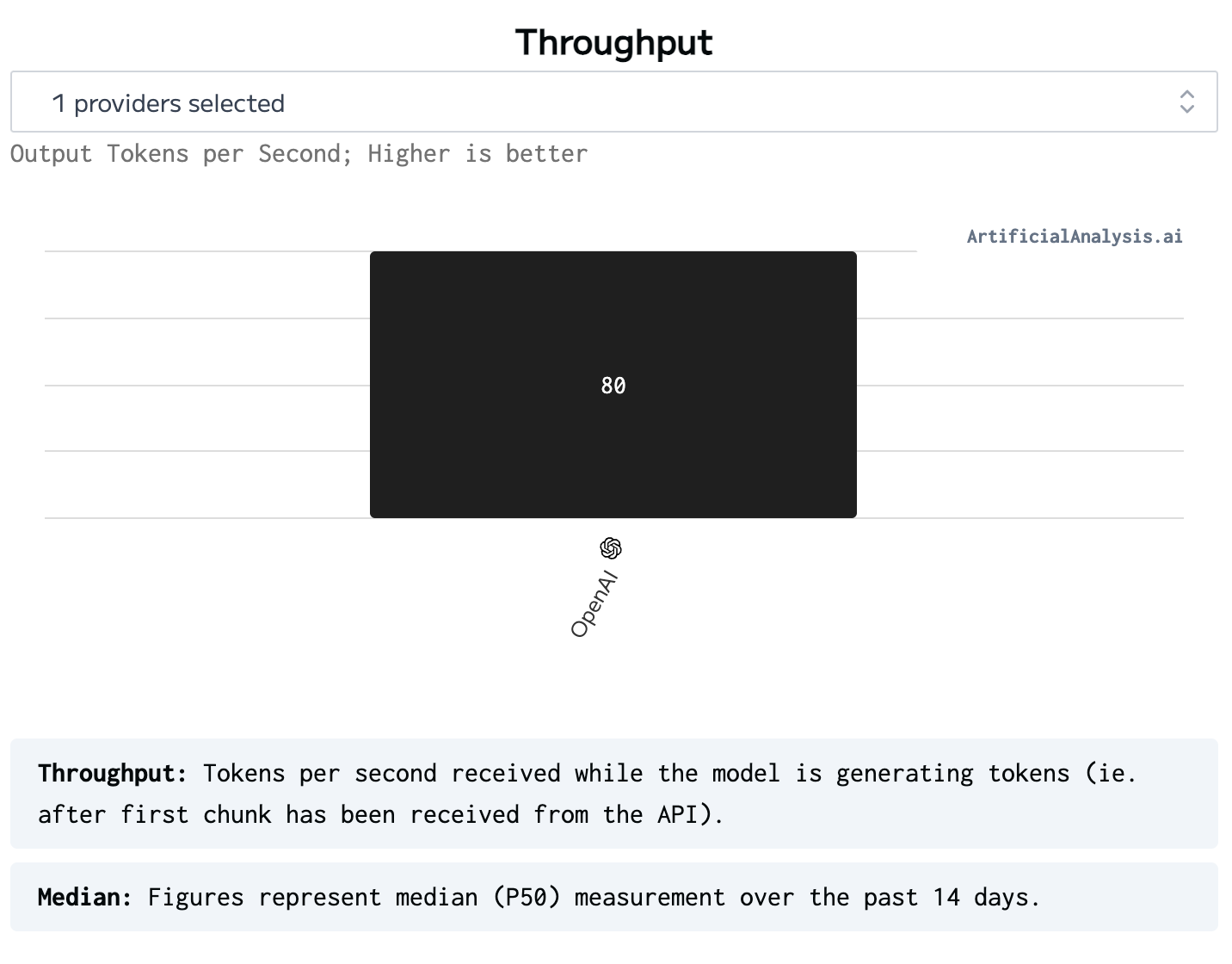 token throughput of GPT4o
token throughput of GPT4o
Conclusion
Now it’s easy.
- AI is not LLM
- You know how LLM works
- OpenAI UI is ridiculous
- If you don’t code, try using some other models or providers for fun
- If you code, you should definitely be looking for using different models and providers depending on your use case
- All LLMs should be open sourced :(
Best,
Gabs